Redefining the 3 Cs - Comfort, Cost, and Creativity in modern housing.

Barndominiums are gaining significant popularity but are not necessarily replacing traditional homes, rather, they’re emerging as an increasingly popular alternative housing option. Here’s what’s driving their growth:
Growing Popularity Since 2020
Google Trends data shows a steady rise in interest in barndominiums, with a notable surge in 2020 that shows no signs of slowing down.
The term “barndominium” has earned its place as a distinct architectural category, similar to colonial, modern, or craftsman styles.
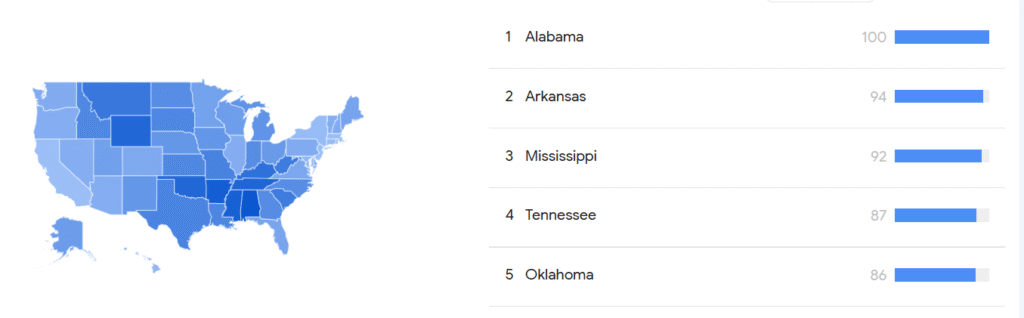
They are most common in the rural Midwest and southern states like Kentucky and Tennessee, but have been popping up all over the United States.
Last 5 Years Interest Graph: Google Trends

USA Top Cities Graph: Google Trends
Why People Are Choosing Barndominiums:
Cost Savings
– Lower overall construction, labor, and materials costs compared to traditionally-built modern homes
– Even though construction materials may be more expensive, labor costs and building time can be significantly lower
– States like West Virginia, Alabama, and Mississippi have costs under $100 per square foot
Energy Efficiency
– Tend to be more energy efficient than traditional homes
– Lower environmental impact, as steel is recyclable and energy-efficient to produce
Durability and Maintenance
– Usually require lower maintenance
– Durable metal exteriors resist routine damage that might plague wood or brick homes
– More economical to maintain over time
Design Flexibility
– Highly customizable with open-floor layouts
– Post-frame construction uses trusses and laminated columns, eliminating the need for interior load-bearing walls.
– Can be built as one- to three-story dwellings
– Tall, soaring rooms with 10′ or 12′ ceilings
Aesthetic Appeal
– Unique rustic-meets-industrial style
– Versatility appeals to DIY-ers and home design enthusiasts
Limitations Preventing Full Replacement
-Despite their advantages, barndominiums face several barriers that prevent them from replacing traditional homes:
Location Restrictions
– Require large pieces of land in rural areas
– Some municipalities have outlawed metal pole structures, citing safety concerns or aesthetic objections
– HOAs may prohibit them
Financing Challenges
– Obtaining mortgages can be more difficult, as lenders are uncertain how to determine the value of non-traditional homes
– May be harder to sell due to their highly customized nature and limited market appeal
Climate Considerations
– Require more winterization efforts than other types of homes
– Insulation costs can vary significantly based on climate zone requirements
Conclusion
Barndominiums are part of a broader trend toward alternative living spaces, alongside tiny homes, shipping container homes, and silo homes, but they’re not replacing traditional homes entirely.
They appeal to a specific market: those seeking rural living, cost savings, customization, and a unique aesthetic.
Traditional stick-built homes continue to provide “enduring value and reliability” and remain the standard choice for most homebuyers, particularly in suburban and urba